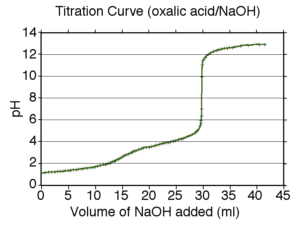
 This is a straightforward neutralisation reaction of both a stong acid (hydrochloric) and a weak acid (ethanoic) by a strong base (sodium hydroxide).
This is a straightforward neutralisation reaction of both a stong acid (hydrochloric) and a weak acid (ethanoic) by a strong base (sodium hydroxide).
The reaction is followed in two ways:
by pH (using an indicator or a pH meter) and
by following the change in conductivity.



